

Shepherd’s deformity is a deformity that develops through osteoporosis and constant microfracture and fracture repair and is associated with limb pain, lameness, and femoral neck fractures ( 5).Ī classification of proximal femoral deformities has previously been proposed based on the largest cohort of patients with fibrous dysplasia known to us. Mechanical stress and repeated fractures result in progressive varus and bowing, typical of shepherd’s curvature ( 4). In 1891, von Recklingosen first described that the proximal femur is one of the most common sites. It can present as simple fibrous dysplasia (70%–80%), polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (20%–30%), Mccun-Albright syndrome (2%–3%), or Mazabraud syndrome(fibrous dysplasia with intramuscular myxoma) ( 3). It accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of benign bone tumors.
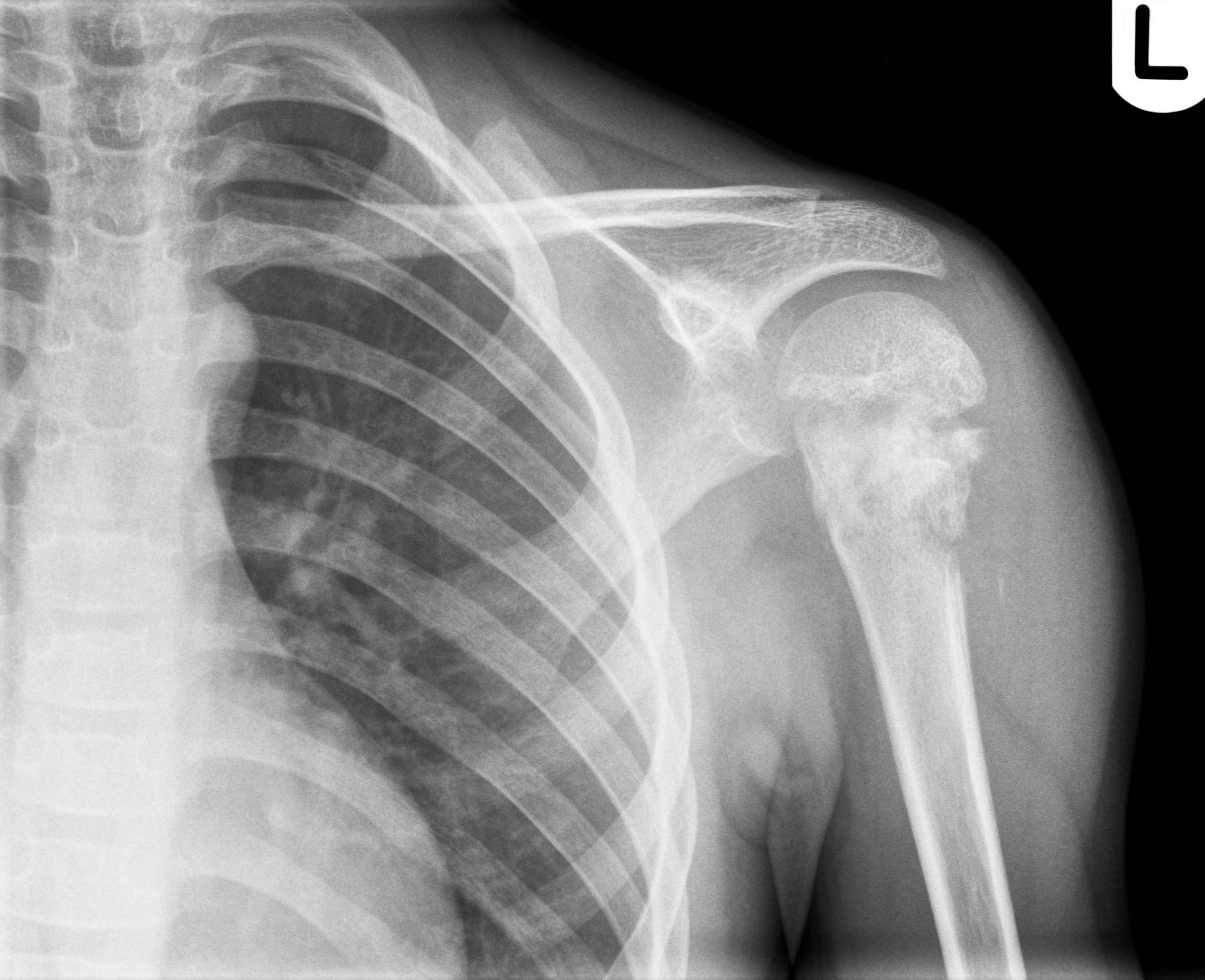
The concept of “fibrous dysplasia” was introduced by Lichtenstein in 1938 ( 1, 2), which is a benign fibrous bone tumor in which fibrous tissue replaces normal bone tissue with metaplastic young woven bone. However, there was still stretch-like pain in the right lower back, but it was tolerable.Ĭonclusions: For patients with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia combined with proximal femoral shepherd deformity and pathological fracture of the femoral shaft with nonunion, osteotomy combined with intramedullary nailing is a simple and convenient way to correct the deformity and obtain correct fracture alignment. One year after the operation, the patient could walk without a walker and take care of himself at home. After six months of re-examination, the patient could walk with a walker. The patient was instructed to gradually bear weight. It was found that the fractured end had a tendency to heal. Three months after the operation, he came to the hospital for re-examination, and an X-ray of the right femur was taken. It is necessary to understand the disease in more detail to avoid overtreatment of benign lesions or misdiagnosis of malignant tumors and other diseases.Ĭase presentation: A 58-year-old man with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, bilateral proximal femur deformity, Shepherd’s angle deformity, right femoral shaft pathological fracture complicated by nonunion, we under fluoroscopy, in the obvious proximal fracture, take osteotomy, and process the shape of the cut bone fragment to adapt it to the corrected force line, and then restore it back to its original position, using intramedullary nailing technology complete the operation. We report a patient with a rare case of multiple fibrous dysplasia combined with proximal femoral shepherd deformity with pathological fracture of the femoral shaft complicated by nonunion. It can manifest as simple fibrous dysplasia (70%–80%), polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (20%–30%), with approximately the same incidence in men and women.

Introduction: Fibrous dysplasia is a benign fibrous bone tumor that accounts for 5% to 10% of benign bone tumors. 2The First Clinical Medical College of Bin Zhou Medical College, Binzhou, China.1Department of Orthopedics, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China.Qifan Yang 1, Jing Liu 2, Lei Tan 1, Ye Jiang 1 and Dong Zhu 1*


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
